Traditionally, most CPS studies have been based on the computer science perspective, focusing on software / hardware issues, without rigorously considering the CPS’s physical processes such as real-time dynamic behaviors. While computing components are key elements in the cyber layer, these alone are not sufficient for diagnosing the entire CPS behavior. On the other hand, the common control theories could not be directly applicable to the CPS physical dynamics which tightly conjoins and coordinates with cyber resources. Therefore, control issues at this layer require new approaches within the context of a unified logical (computing) and physical process model of the CPS.

Distributed Control Estimation Synthesis
- Main Concern: Computing optimal distributed control law is computationally intractable due to network topological constraints in multi-agent systems
- Research Goal: Develop optimal distributed control and estimation laws for
- Arbitrary network topology
- General higher-order systems
- Stochastic model
- Performance guarantee with respect to the known global optima
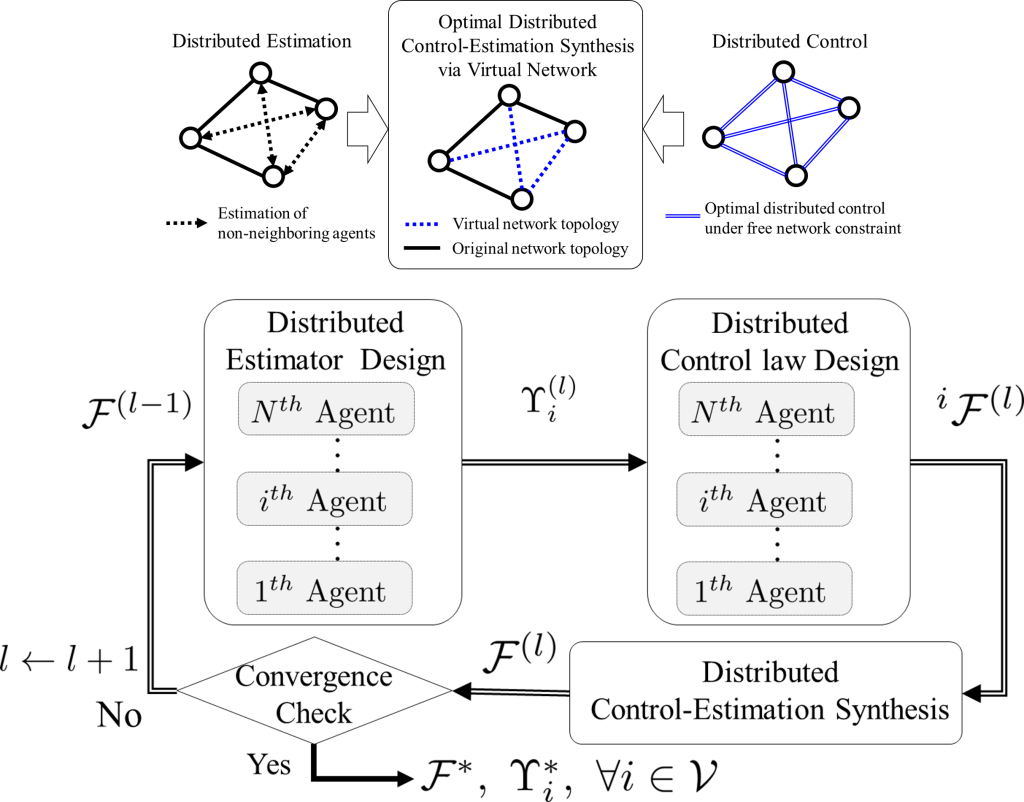
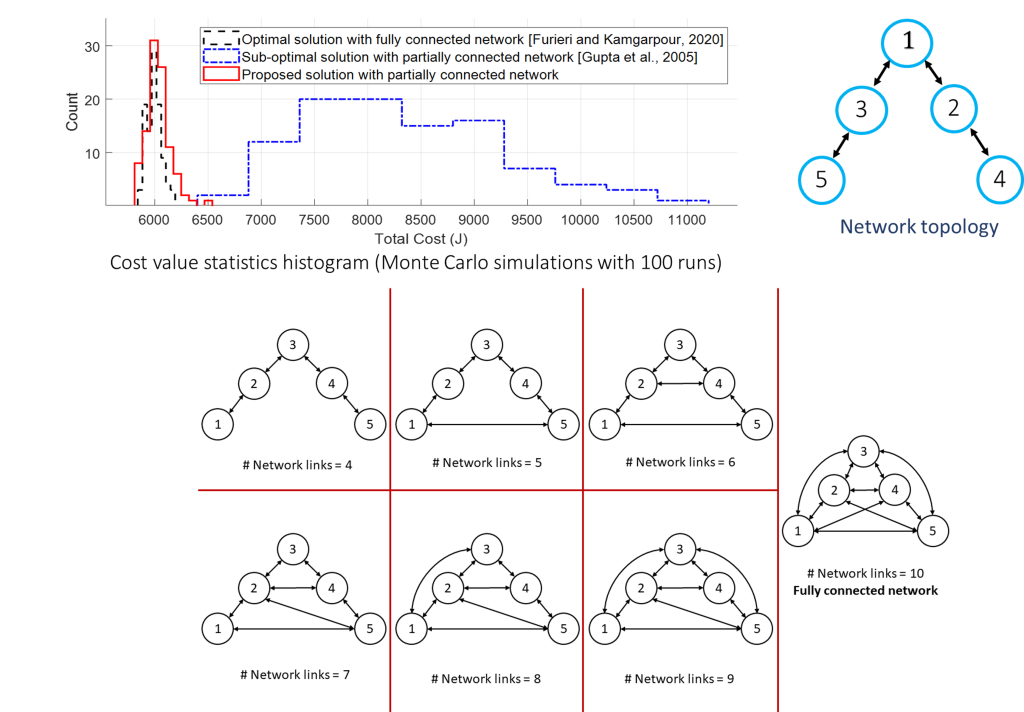
- Illustrative Example: Proposed method match the fully connected network case (globally optimal solution) despite the network topological constraints
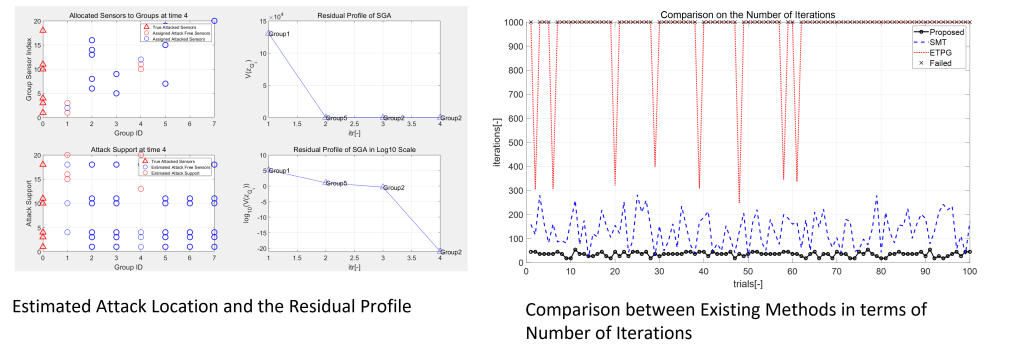
Secure State Estimation (SSE) against Sparse Sensor Attacks
- Main Concern: Sparse sensor attacks inject false or misleading data into a limited number of sensors, which can cause the system to malfunction or make incorrect decisions based on incorrect data
- Research Goal: Reconstruct the actual state and the attack when CPS is injected with sparse sensor attacks
- The solution of the SSE problem generally can be obtained by solving L0 minimization problem
- Main difficulty: The L0 minimization problem is NP-hard problem
- Relax the computational complexity by alternating gradient-descent step and projection step
- Accelerate the computation by adopting heuristic ideas such as broadcasting and sequential greedy algorithm
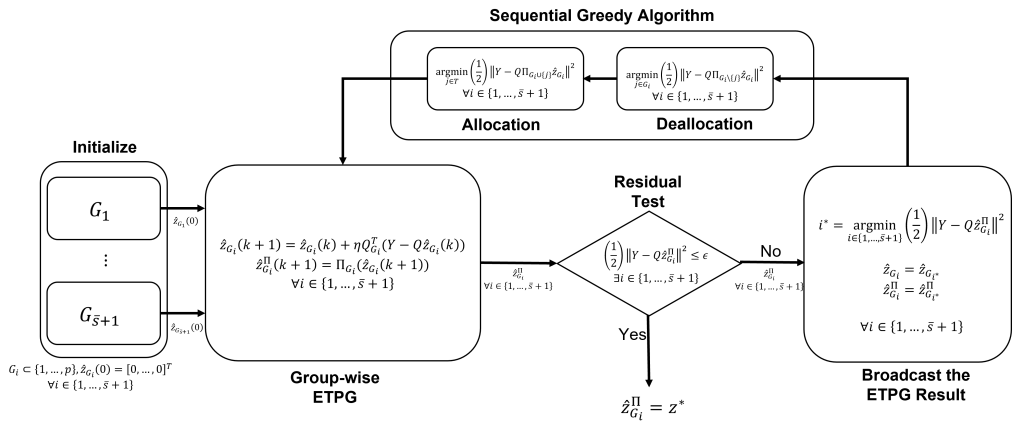
- Illustrative Example: Comparison result of the proposed algorithm in presence of sensor attacks
CPS Architectural Vulnerability
- Main concern: Under certain CPS architecture, it is possible that a certain abnormal behavior could avoid causing a large variations in the residuals while increasing state estimation error
- Research Goal: Development of an analysis methodology against potential undetectable anomalies.
- Derivation of mathematical conditions for testing CPS architectural vulnerability against undetectable anomalies
- Design and demonstration of undetectable anomalies
- Illustrative Example: Error on the navigation module in UAS autopilot
- Malicious backdoor virus can modify the guidance logic to drive the UAS to a different path than the intended waypoint
- The view reported to the ground station is normal, implying the anomaly undetectable!
CPS Monitoring System Development
- Main concern: Fault-tolerant state estimators and fault detection scheme cannot guarantee the detection of all possible anomalies
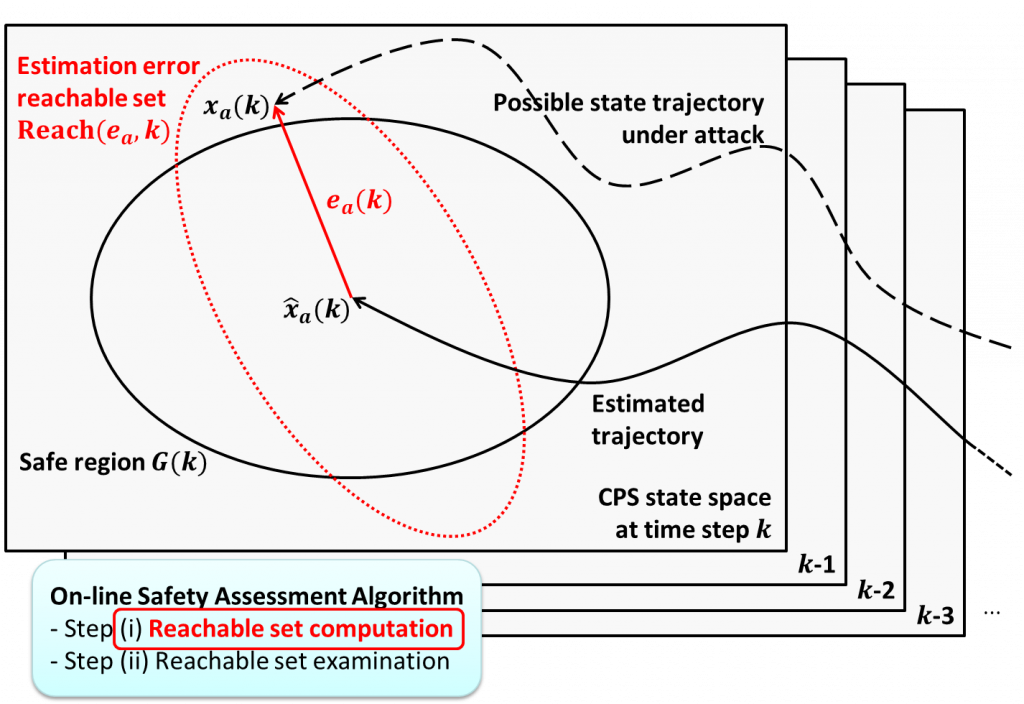
- Research Goal: To ensure the safety of CPS against against potential undetectable anomalies using reachability analysis.
- Compute the reachable set of CPS states possibly deviated by all potential cyber attacks
- Compare all the possible deviations of CPS states with the preset safe region
- Main difficulty: reachable set computation typically demands large computation cost and thus has mostly relied on the approximation techniques
- On-line Safety Assessment Algorithm
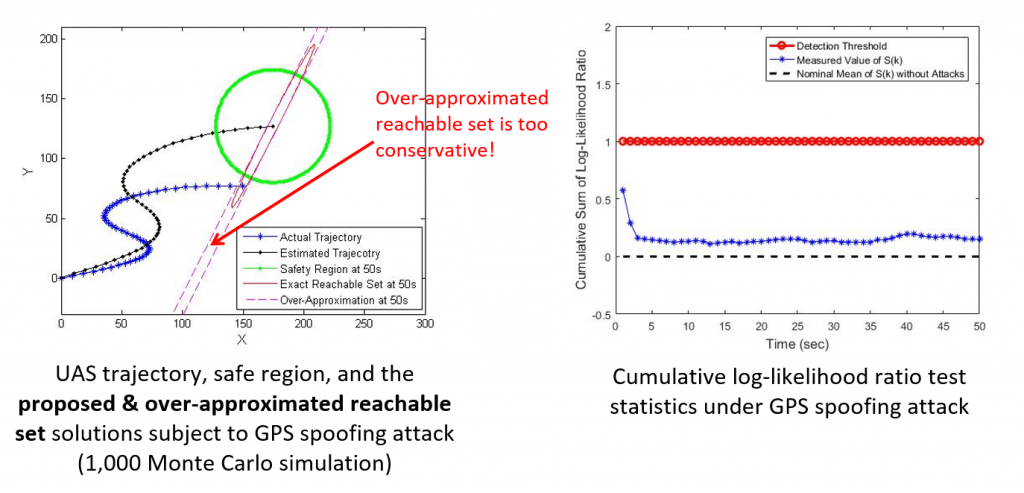
- Analytically derive the exact reachable set solution which is more accurate and reliable
- Establish recursive computation structure which is computationally efficient
- Successfully complement the attack detection-monitoring systems already in place in the CPS
- Illustrative Example: on-board navigation module is subject to GPS spoofing attack which is not detectable
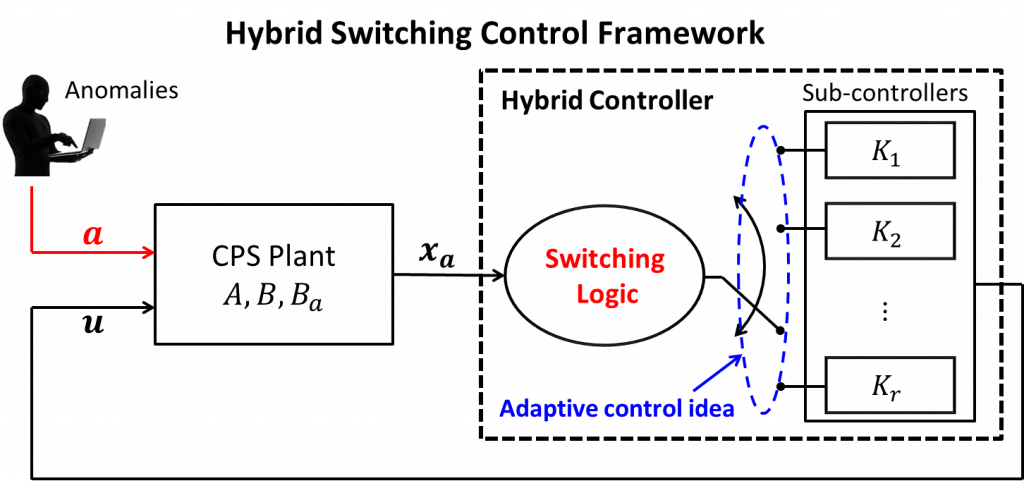
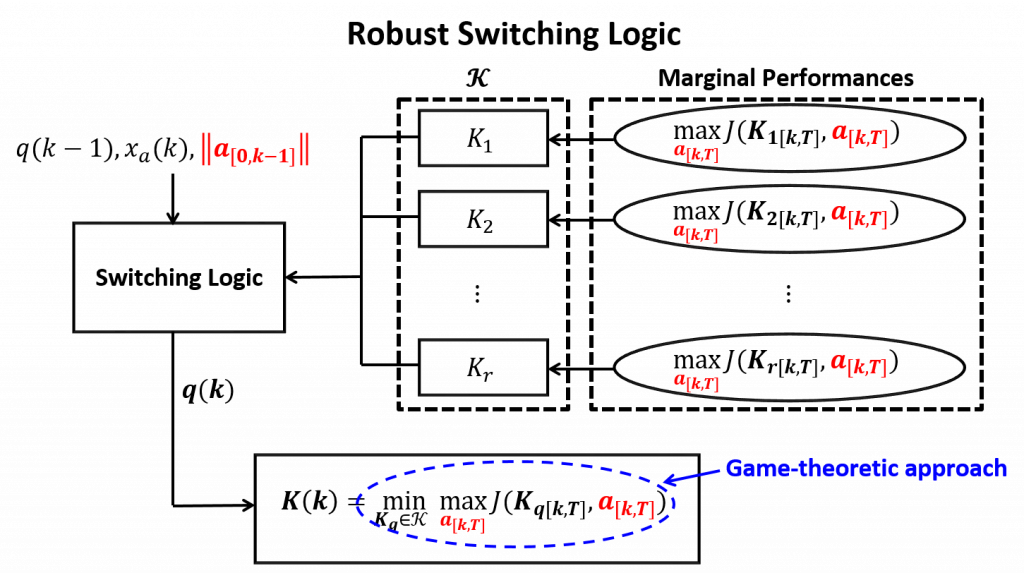
CPS Control Strategy against Unpredictable Anomalies
- Main concern: Designing controllers against a priori unknown anomalies may degrade the CPS performance if the actual anomaly deviate from the one assumed by a controller
- Research Goal: Develop hybrid controller which consists of multiple sub-controllers, each matched to different anomalies
- Design of the robust switching logic to switch among the multiple controllers to the most safe sub-controller against unpredictable anomalies
- Combine adaptive control idea and game-theoretic approach to acheive both safety and performance of CPS
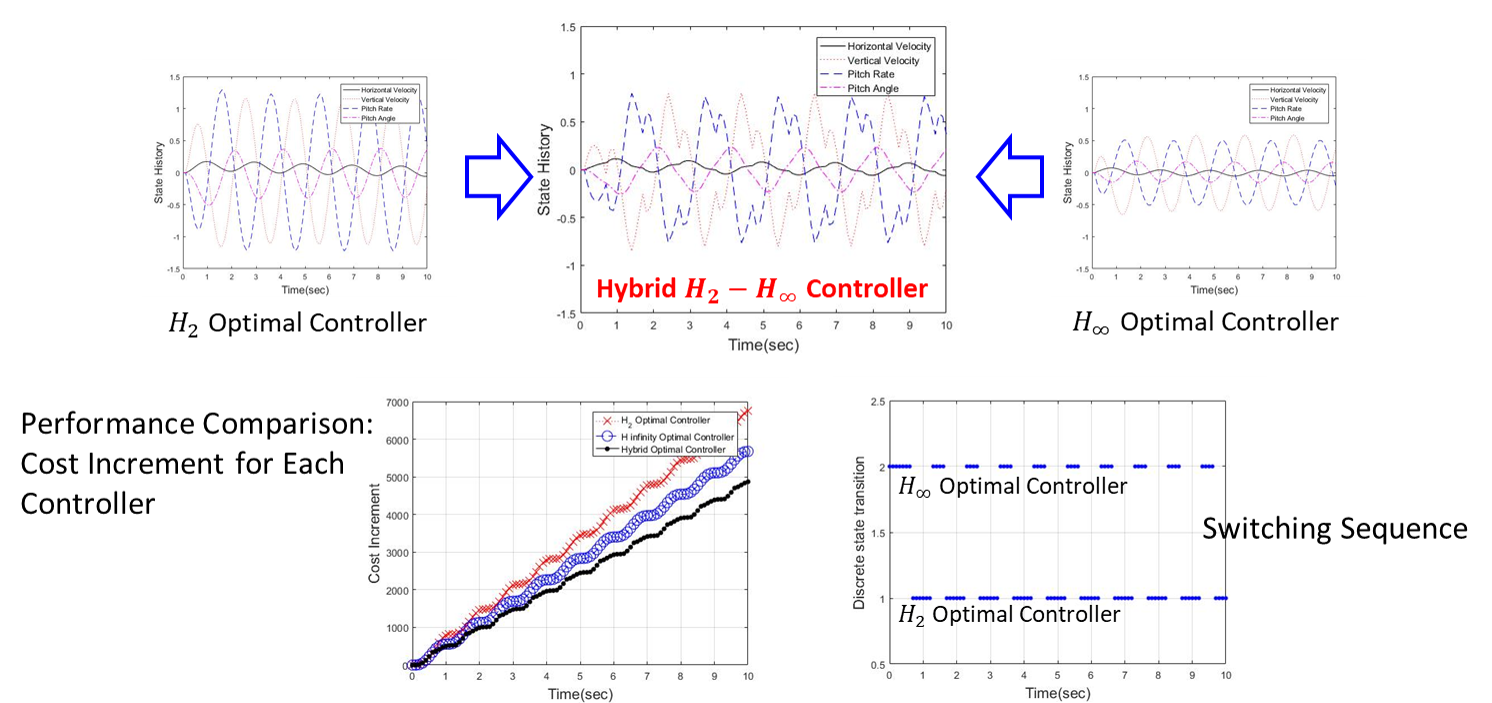
- Illustrative Example: Hybrid H_2-H_infinity controller applied to UAS rotorcraft subject to sinusoidal bias injection
- H_2 optimal controller addresses the average effect of anomalies
- H_infinity optimal controller addresses the worst effect of anomalies
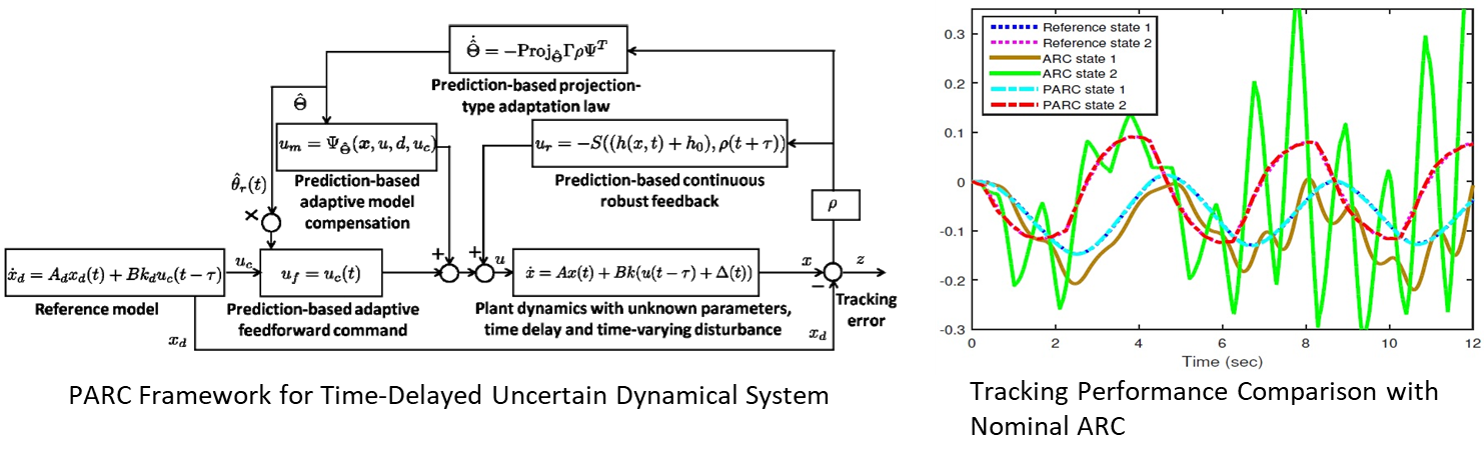
CPS Control Strategy against Network Delay
- Main concern: CPS control of uncertain dynamics model subject to the simultaneous presence of parameter variations, disturbances, and control input delay
- Research Goal: Develop a control structure to simultaneously compensate for all the system uncertainties with rigorous stability and performance guarantees
- Predictor Adaptive Robust Controller (PARC): Combine prediction-based robust nonlinear feedback and prediction-based adaptation law